Loosening
As pain and disability due to loosening become severe enough to require
revision arthroplasty, abnormalities in the binding of the cement to the bone or
prosthesis are almost always visible radiographically.
Radiographic abnormalities include:
- Progressive and extensive widening of interfaces between bone-cement,
bone-prosthesis, or cement-prosthesis.
- Fragmentation or fracture of cement.
- Migration of prosthetic components
Absence of these findings requires consideration of other sources for painful
arthroplasty.
INTERFACE WIDENING
Localized by Gruen zones
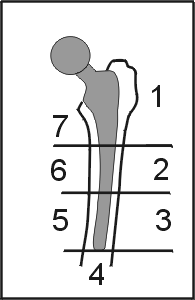 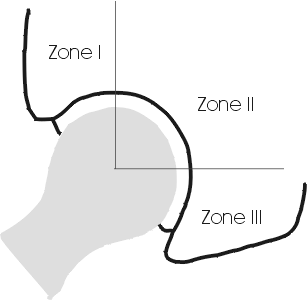
INTERFACE WIDENING
-
Assessment of width
- Radiolucent zones wider than 2 mm are evidence for loosening
- Radiolucent zones less than 1 mm are acceptable
- Radiolucent zones less than 2 mm that are stable and not progressive after
6-12 months and clinically asymptomatic should not be considered a sign of
loosening
- Always compare with baseline study
- Radiolucent zones on baseline studies can be secondary to:
- Poor cement packing
- Interposition of blood or fibrous tissues
- Movement of prosthesis before cement has polymerized
-
Assessment of location
- Acetabular component
- 1-2 mm radiolucent zone cement-bone interface of superolateral aspect (Gruen
zone 1) are frequently seen and not a sign of loosening.
- Radiolucent zones at cement-bone interface of the inferomedial aspect of the
acetabular component (Gruen zone 3) are more ominous and usually represent
loosening or potential loosening
- Femoral component
- Thin lucencies about superolateral aspect of femoral component (Gruen zone 1)
extending for a few cm is common follow up finding, when seen alone is not
clinically significant.
- Wide lucencies about superolateral aspect of femoral component (Gruen zone 1)
is strong radiographic evidence of loosening (Miller, Burke)
.jpg)
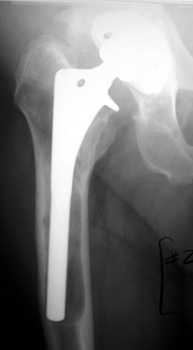
LOOSENING WITH FEMORAL COMPONENT IN VARUS
Marked interface widening Gruen zone 7
LOOSENING
Cemented components
- Normal findings
- 1-2 mm lucent zones at cement interfaces.
- Do not represent loosening if they do not progressively widen
- Indicative of loosening
- > 2 mm lucencies
- Cement fracture
- Diagnostic for loosening
- Migration or change of position of component
- Subsidence
|
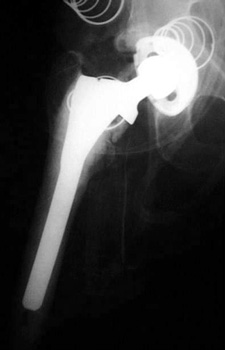
|
|
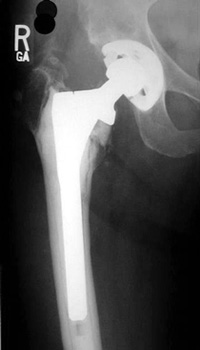
|
9/91
|
10/94
|
11/95
|
|
Progressive interface widening |
LOOSENING
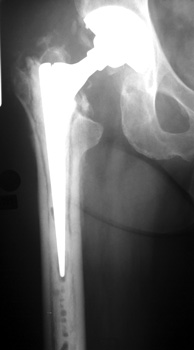
No prior studies available. Abnormally widened interfaces surrounding entire cement mantle of femoral
component, consistent with loosening.
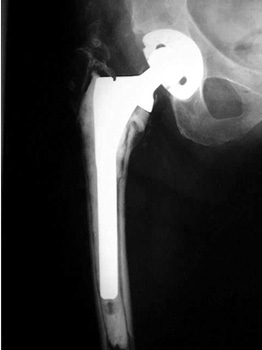
LOOSENING
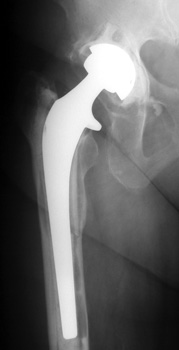
No prior studies available. Abnormally widened interfaces about femoral component at Gruen zones 1, 6,
and 7. Osteolysis at Gruen zone 5 with marked thinning of femoral cortex placing
patient at risk for pathologic fracture.
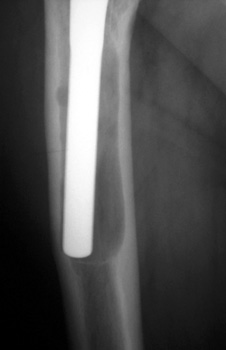
Cement fracture Gruen zone 6 close up next slide
CEMENT FRAGMENTATION
May occur with shift of femoral component.
Transverse fractures of cement near distal femoral stem seen in up to 1.5% of
THR, associated with mild subsidence. If less than 4mm, usually not associated
with failure. (Weber and Charnley)
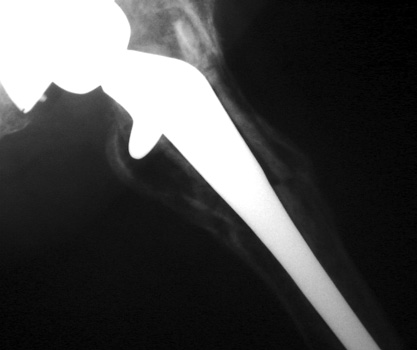
CEMENT FRACTURE
LOOSENING
Non cemented components
- Normal
- 1-2 mm lucent zones at interfaces normal
- Calcar resorption
- Cortical thickening or periosteal reaction
- Non progressive mild subsidence (< 1 cm ) of femoral component
- Indicative of loosening
- Progressively widened lucent zones at interfaces > 2 mm.
- Bead shedding
- Endosteal scalloping
- Diagnostic for loosening
- Migration or change of position of component
- Progressive subsidence of acetabular or femoral component
ENDOSTEAL SCALLOPING
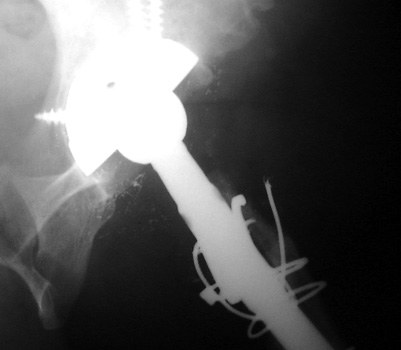
BEAD SHEDDING
BEAD SHEDDING
LOOSENING
COMPONENT MIGRATION
- Motion of any component is diagnostic of loosening.
- This sign appears slowly, requiring comparison with baseline or the oldest
studies available.
- Obviously abnormal component positioning without comparison studies is
adequate for diagnosis of loosening
 |
|
|
10/01 |
11/01 |
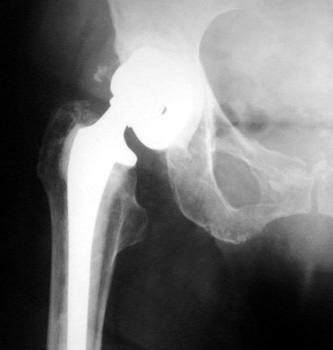
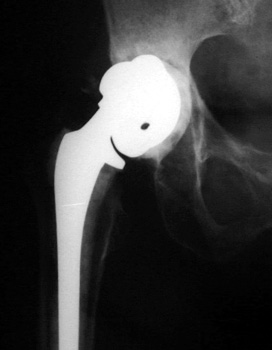
COMPONENT MIGRATION
ACETABULAR CUP
ACETABULAR COMPONENT
Progressive protrusio and tilt
|
|
|
|
2/00 |
1/01 |
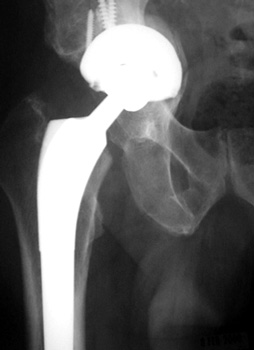
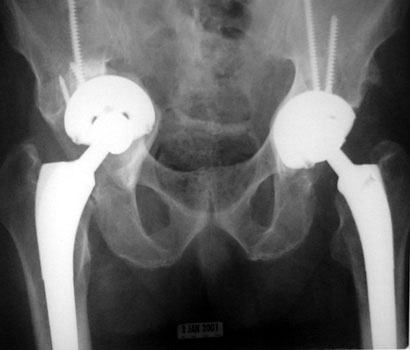
ACETABULAR COMPONENT
Migrating acetabular cup
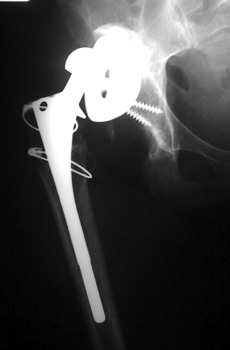
Very abnormal positioned cup. No comparison radiographs were available.
Current radiographs demonstrates markedly tilted cup which has migrated
laterally from pelvis.
 |
 |
|
12/93 |
8/98 |
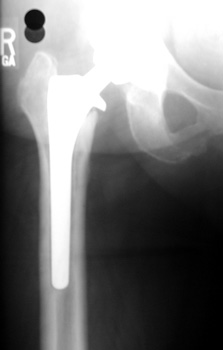
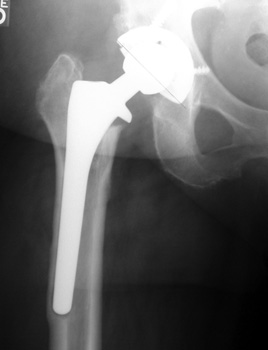
MIGRATION
FEMORAL COMPONENT
SUBSIDENCE
- Sinking of component over time
- Femoral component
- Stem sinks into femur
- Trochanter position too proximal
- Acetabular component
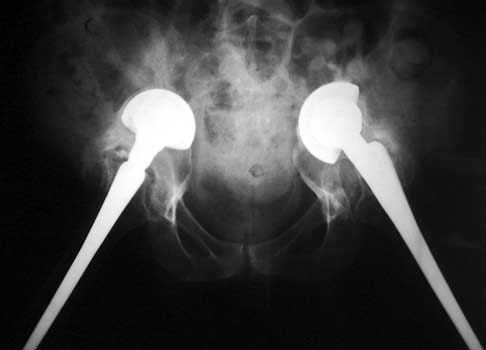
ACETABULAR COMPONENT
Severe protrusio in patient with RA
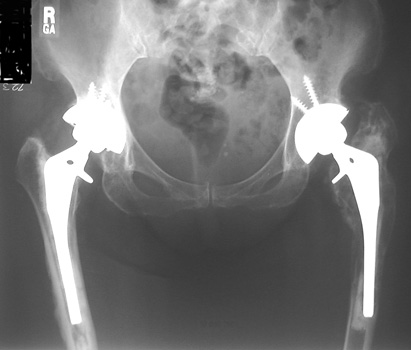 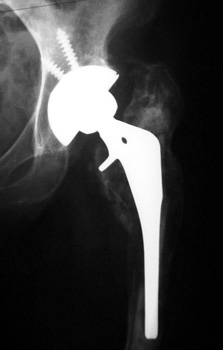
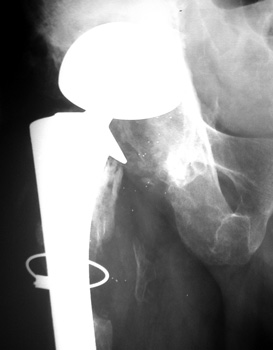
SUBSIDENCE - loose femoral prosthesis with interface widening,
osteolysis Gruen zone 6, cement fracture left femoral component
and osteolysis, with femoral component in valgus.
| 












