OSTEOARTHRITIS
non-inflammatory deterioration of articular cartilage with articular surface
and marginal bone formation.
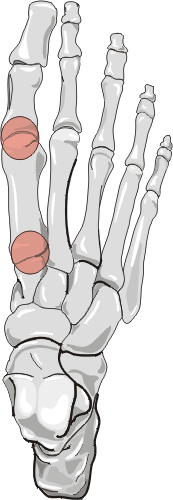
1. Distribution
The first metatarsal phalangeal and first tarsometatarsal joints are most
commonly affected with osteoarthritis of the foot. The dorsal talonavicular
joint is also commonly involved. The remaining metatarsal phalangeal and interphalangeal
joints are affected to a lesser degree. Plantar or posterior calcaneal spurring
may also occur. The disease distribution may be uni- or bilateral.
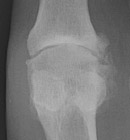
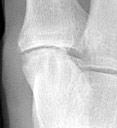
2. Erosion pattern
Radiographic manifestations may include marginal osteophyte and subchondral
bony cyst formation, eburnation, and interosseous joint space narrowing. First
metatarsal phalangeal joint osteoarthritis is frequently associated with hallux
valgus deformities. Calcaneal spurs, when manifested, are sharp and well defined.
3. Differential
diagnosis
Joint space narrowing and sclerosis at the tarsometatarsal joint,
or metatarsal phalangeal thickening and subchondral cyst formation may be
confused with gout. Inflammatory disease may also be present for a subset
of patients.