Septic arthritis in the diabetic foot usually arises from contiguous osteomyelitis
spreading into the joint. Occasionally septic arthritis may arise from penetrating injury
into the joint. Joint space narrowing and destruction ensues, accompanied by joint
effusion. The septic joint fluid may communicate with adjacent structures such as tendon
sheaths.
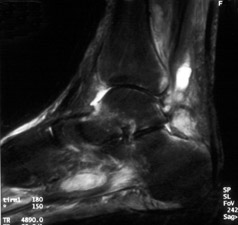 55-year-old man with
long standing diabetes. He had ulcer formation of the posterior ankle and hindfoot, with
markedly swollen ankle. Sagittal STIR image demonstrates ankle effusion and reactive bone
marrow edema at the anterior and posterior aspects of the distal tibia, anterior and
posterior talus, and superior calcaneus. These represent the "bare areas" of the
ankle joint where protective articular cartilage ends. These areas are the first to show
marrow signal change in inflammatory and/or infectious arthritis. (Click on the
image to see a larger version)
55-year-old man with
long standing diabetes. He had ulcer formation of the posterior ankle and hindfoot, with
markedly swollen ankle. Sagittal STIR image demonstrates ankle effusion and reactive bone
marrow edema at the anterior and posterior aspects of the distal tibia, anterior and
posterior talus, and superior calcaneus. These represent the "bare areas" of the
ankle joint where protective articular cartilage ends. These areas are the first to show
marrow signal change in inflammatory and/or infectious arthritis. (Click on the
image to see a larger version)
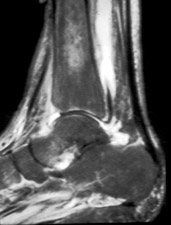
A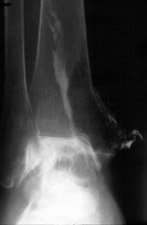 B
B
A. Sagittal STIR image of patient with septic tibio-talar joint. The joint fluid
communicates with the flexor digitorum longus tendon, dissecting proximally to form an
abscess in the muscle belly. B. Arthrogram performed after aspiration of joint demonstrates contrast in the tendon
sheath as well in a sinus tract which dissects out medially. (Click on the images to see larger
versions)