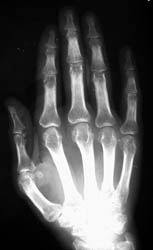
 Multicentric
reticulohistiocytosis is a rare systemic disease with (proliferation)
of histiocytes which leads to destructive polyarthritis and skin lesions.
Multicentric
reticulohistiocytosis is a rare systemic disease with (proliferation)
of histiocytes which leads to destructive polyarthritis and skin lesions.
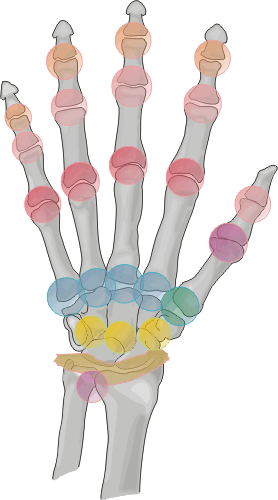
Distribution:
Target areas of the hands primarily involve the interphalangeal joints, especially
at the DIPs. The MCP joints and carpal bones are involved less frequently.
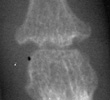
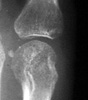
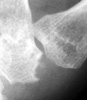
Radiographic Appearance:
Symmetric well-circumscribed marginal erosions are seen at the involved articular
surfaces. Uncalcified soft tissue nodules and the absence of peri-articular
osteoporosis are additional radiographic features of multicentric reticulohistiocytosis.
Severe progression of the disease can lead to extensive osseous resorption
with foreshortening of the fingers and telescoping digits.
Differential Diagnosis:
Radiographic findings in multicentric reticulohistiocytosis are different
than those in rheumatoid arthritis since there is involvement of the joints
distally. Multicentric reticulohistiocytosis can also be differentiated from
other arthritides due to the absence of juxtaarticular osteoporosis and periosteal
reaction. The erosive pattern seen in gout and psoriatic arthritis is unlike
multicentric reticulohistiocytosis due to their asymmetric distribution. Furthermore,
calcified soft tissue nodules and overhanging edges are findings in gout which
are not seen in multicentric reticulohistiocytosis.